Pronouns do the grammatical heavy lifting in English, enabling our sentences to read well and not sound like we are repeating ourselves, using the same nouns over and over again.
Some of the different categories that pronouns fall into include subject pronouns and they are very fundamental in making up properly understood grammatically composed sentences.
This article shall define what is a subject pronoun and also instruct you on using subject pronouns to enhance your writing and speech.
Key Takeaways
- Subject pronouns (I, you, he, she, it, we, they) replace nouns as the doers of actions in sentences, helping avoid repetition and maintain sentence clarity.
- They differ from object pronouns (me, him, her, us, etc.), which receive the action—understanding this distinction is essential for grammatical accuracy.
- Correct use of subject pronouns involves proper sentence placement, noun substitution, and subject-verb agreement, especially in complex or compound sentence structures.
- Students can improve their understanding using grammar-enhancing tools like Ask AI, and check accuracy and clarity of pronoun use with Undetectable AI’s grammar checker or AI-powered writing assistant.
- Using Undetectable AI also helps students humanize overly formal or robotic grammar exercises, making explanations and practice writing more natural and effective for real-world communication.
What Are Subject Pronouns?

A subject pronoun (also a nominative pronoun) is used as the subject of a verb.
This implies that it symbolizes the individual/individuals or the object that does the action being documented.
It can usually be found at the beginning of the sentence, preceded by a verb due to this.


Never Worry About AI Detecting Your Texts Again. Undetectable AI Can Help You:
- Make your AI assisted writing appear human-like.
- Bypass all major AI detection tools with just one click.
- Use AI safely and confidently in school and work.
Subject pronouns should be thought of as the heroes who are taking action but in place of repetitions.
For example, if we write “Maria went to the store and Maria bought groceries,” it sounds repetitive and we can fix a more natural flow by referring to Maria using the subject pronoun.
This will sound like “Maria went to the store, and she bought groceries.”
The use of subject pronouns makes our language lean and non-repetitive.
They save us the humiliation of repetitions that would otherwise occur in a sentence or paragraph in which we are bound to have to repeat the same noun once or more.
Subject vs. Object Pronouns
English grammar depends mostly on the distinction between what is subject pronoun and object pronoun.
The doer of an action in a sentence is the subject pronoun whereas the recipient (receiver) is the object pronoun.
This difference holds the clue as to the form you have to adopt in writing a pronoun in a given situation.
Such words as I, you, he, she, it, we, and they are referred to as subject pronouns. These pronouns are usually the subject of a sentence or clause.
Object pronouns are words that replace nouns functioning as the object of a verb or preposition in a sentence.
They include me, you, him, her, it, us and them.
Examples are given below:
Consider these examples to see the difference:
- “She called him.” (She = subject pronoun, him = object pronoun)
- “They invited us to the party.” (They = subject pronoun, us = object pronoun)
- “I gave her the book.” (I = subject pronoun, her = object pronoun)
- He told them the news.” (He = subject pronoun, them = object pronoun)
- “We saw you at the concert.” (We = subject pronoun, you = object pronoun)
- “It surprised me completely.” (It = subject pronoun, me = object pronoun)
- “You reminded her about the meeting.” (You = subject pronoun, her = object pronoun)
- “She helped us with the project.” (She = subject pronoun, us = object pronoun)
- “They thanked him for his assistance.” (They = subject pronoun, him = object pronoun)
List of Common Subject Pronouns
English has seven main subject pronouns, each serving a specific purpose in sentence construction.
Below are some of these categories:
- First Person Singular: The pronoun “I” is the speaker or writer every time. It is strange since it is never capitalized in English in the smallest letters regardless of how it is applied in the sentence.
Example:
1. I like reading mysteries
2. I am struggling to comprehend what you say. - Second Person Singular and Plural(You): The word “you” is a flexible one since it can be used to mean many people or even a single individual. But the context applied makes it evident whether the individual you are talking to is a single individual or a group of individuals.
Example: You are invited to the celebration.
- Third Person Singular (He, She, It): They are pronouns directed to people, animals or objects not directly involved in the conversation. He is commonly used to mean a male, she refers to a female and it refers to an object, animal or something abstract.
Example:
1. He runs every morning
2. She loves classical music
3. It needs repair
4. It insists on itself
- First Person Plural (We): These pronouns are used when the speaker is referring to themselves and at least one other person.
Example: We decided to postpone the meeting.
- Third Person Plural(They): “They” is used to point out more than one and to denote a person, animal, or object that is not of primary focus in the conversation. It can also be used as a single pronoun by people who need to be identified in a gender-neutral language.
Example: They arrived early for the concert.
Many students wonder about subject pronouns in other languages, particularly what is a subject pronoun in Spanish.
While Spanish has similar concepts, the pronouns differ. For instance, “I” means “yo”, “tú/usted” (you), “él/ella” (he/she), “nosotros/nosotras” (we), and “ellos/ellas” (they).
However, the Spanish language often omits subject pronouns since the verb conjugation indicates the subject.
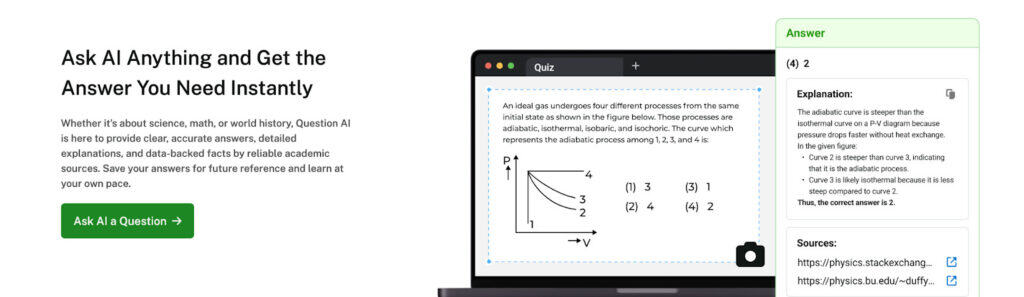
We recommend Ask AI to help students test their understanding of personal and subject pronouns in real time.
This is because its interactive nature combined with immediate feedback makes it incredibly likely to increase the cognition and application of pronounced pronoun recognition and usage.
How to Use Subject Pronouns Correctly
To learn how to use the subject pronoun, a person ought to acquaint oneself with three major tenets, i.e, the right place of pronouns in a sentence, the mechanisms of employing the noun to be substituted and a standard subject verb connection.
The details of each principle are given in brief below:
Sentence Position and Subject Role
Subject pronouns are words that replace the subject of a sentence, indicating who or what is performing the action.
Example: She has a beautiful voice.
In questions, the subject pronoun might follow an auxiliary verb.
Example: “Does he play guitar?
Although in a sentence like this that has two or more clauses, there is still a subject to each clause.
Example: When she comes, we shall begin the presentation.
Knowing sentence position will make you avoid such simple errors as an object pronoun in subject position.
As an example, a sentence like “Him and I went shopping” is wrong, because “him” is an object pronoun. The right one is “He and I went shopping.”
Replacing Nouns for Clarity
The pronouns should refer to the nouns so as to prevent repetition and to present a clear picture.
The trick is that your readers must understand what or whom the pronoun is referring to at all times.
This relationship between a pronoun and a noun is referred to as an antecedent agreement.
In the replacement of nouns with pronouns, the space between the noun and the pronoun should be borne in mind.
In case there are many words between them, or there are several nouns that may answer to the antecedent, readers may be confused.
Here, the repetition of the noun will be better viewed in the situation than the pronoun.
For instance, as presented in the sentence, John said to Mark that he would assist in the project, but it is not clear if he is saying this to Mark or John.
One would phrase it out in a more direct way as John told Mark, John would help on the project.
Subject-Verb Agreement Rules
The subject pronouns must agree with their verbs in number and person.
It is an effective way to help you correct those grammatical errors and help the reader to better understand you.
The singular subject pronouns (I, you, he, she, it) have singular subjects and the plural subject pronouns (we, you, they) include plural subjects.
The first-person pronoun has peculiar rules and usually interprets plural forms of verbs, although it should speak of a single entity.
Example: “I am,” “I were” (in subjunctive mood), I have.
The pronoun you is used either in a singular or in a plural meaning, it fits easily in situations where it may mean one or otherwise, such as in sentences like ‘you are,’ ‘you were,’ ‘you have’.
The third-person singular pronouns (he, she, it) have a different structure, as verbs in present tense are parts of the grammar with the suffix “-s” (he runs, she writes, it works) as opposed to the plural subjects which do not apply the suffix ‘-s” to plural subjects.
To guarantee commonly correlated sentences, we recommend using Grammar Checker to ascertain the use of the subject-verb agreement and how to position the pronouns.
These devices will notice mistakes that may escape the eye during proofreading and allow you to sharpen your intuition of the right guidelines.
Subject Pronouns vs Object Pronouns
The distinction between the subject and the object pronouns may be regarded as one of the most significant English grammar ideas.
Study the key difference and become an expert who creates more correct sentences grammar-wise.
Key Differences in Function
Subject pronouns do action, whereas object pronouns either receive action or are prepositions of objects.
It is this functional disparity that will dictate the type of pronoun structure that you employ at any particular moment.
Subject pronouns serve to respond to the question who or what is doing something, whereas object pronouns serve to respond to the question to whom, or to, or to whom or what is something being done.
It is the grammatical role but not the meaning of the word, that dictates the pronoun to be used.
Example: She gave him the book
The subject pronoun is ‘she’ since it indicates who did the giving of the book.
The object pronoun is him since it states to whom the action was done.
This difference is significant especially in compound subjects and objects. There are many speakers who will say “Me and her went to the store” when they need to say “She and I went to the store.”
The misunderstanding exists since there is at least some use of pronoun forms by people as they sound correct, rather than their grammatical function.
Examples in Parallel Sentences
By making parallel sentences, one can see the difference between subject and object pronouns. Here is the version with the subject pronoun and the object pronoun form:
- Subject Pronoun: I called up Sarah yesterday.
- Object Pronoun: Sarah phoned me yesterday.
In the first sentence, the subject referring to the call happens to be “I.” In sentence two, the object that is subjected to the action of calling is referred to as “me.”
Pronoun Substitution Test
The substitution test is a sure way of establishing which one to use, subject or object pronoun.
The method is to temporarily eliminate the pronoun in favor of the noun in order to know what makes grammatical sense.
When dealing with compound subjects, simplify the decision by testing each pronoun individually. Remove the other subject and see which pronoun works alone.
An example is ‘ I went to the store,’ and not ‘me went to the store,’ which is incorrect. Using the same logic, it should be written like this: ‘John and I went to the store.’
Existing components will do the same test to compound objects.
The teacher gave John and me extra credit is correct in the sense that the” teacher gave me” extra credit makes sense but ‘the teacher gave I an extra credit’ does not.
Subject Pronouns in Questions and Answers
Questions and answers pose special difficulties in the matter of the use of subject pronouns. In yes/no questions, auxiliary verbs normally precede the subject pronoun:
“Are you coming to the party?”
“Will she be able to complete the project in time?”
“Hallo, are they there?”
The subject pronoun still has its purpose, despite not being put in the position where it is normally placed.
Wh-questions (who, what, when, where, why, how) are sometimes more difficult. A subject pronoun is used when a question is the subject. For instance,
“Who is calling?” demands not “Him is calling,” but “He is calling” or “She is calling” as a reply.
Normal relations between the subject and the object exist when the question word is not the subject.
Example: “Who saw you?” “I saw him.”
In an informal style of speech, it is typical to encounter a lot of people expressing not only the subjective form, but the objective as well, of the word who.
Who (subject) and whom (object), is however, observed in formal writing. Understanding whats a subject pronoun helps you navigate these formal requirements.
Responses to inquiries are to have correct subject-object relations. When a person poses the question, “Who won the game? The correct subject pronouns used are the answer:
They did or We did. Do not use phrases such as “Them did” or “Us did,” combining the use of object pronouns and subjects.
Don’t leave without exploring our AI Detector and Humanizer in the widget below!
Final Thoughts
Subject pronouns are essential to English sentences; without them, clear communication and grammatical accuracy wouldn’t be possible.
It does not matter whether you are asking what’s a subject pronoun or want to polish up on your general grammar skills, mastering those necessary words will help boost your communication performance.
In case you still feel confused after reading this, try Undetectable AI and find more advanced grammar tools and AI-powered writing assistance.
