Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping the job market. It’s creating new opportunities and challenges.
We’re witnessing a transformation in how we work. For the past few years, its impact on employment has been a hot topic, sparking debates worldwide.
Some fear AI will replace human workers. Others see it as a tool for enhancement. The truth likely lies somewhere in between.
We’re entering an era of human-AI collaboration. It’s crucial to understand the implications.
This article explores AI’s impact on jobs. We’ll look into current trends and future predictions, discuss the challenges we face, and explore potential solutions.
By understanding these factors, we can better prepare for the future. We’ll need to adapt our skills and policies. It’s essential for a smooth transition into an AI-driven economy.
Let’s explore the complex relationship between AI and employment. We’ll consider how it’s changing the way we work and what it means for our future careers.
The Evolution of AI and Employment
AI has been around for decades, but recent advancements have accelerated its impact. Machine learning and deep learning have transformed AI’s capabilities—making it more powerful and versatile.
Machine learning used to be a niche field, primarily focused on creating algorithms that could learn from data and make predictions.
In its early stages, AI was limited by the computational power available and the simplicity of its models.


Never Worry About AI Detecting Your Texts Again. Undetectable AI Can Help You:
- Make your AI assisted writing appear human-like.
- Bypass all major AI detection tools with just one click.
- Use AI safely and confidently in school and work.
It relied heavily on rule-based systems and linear regressions.
These early systems could handle only narrow, specific tasks, such as recognizing patterns in datasets or performing basic classifications.
This tech has made significant leaps forward, especially in the past few years.
There’s a growing role in various industries, with AI now performing tasks once thought impossible for machines.
From diagnosing diseases to writing news articles, AI’s reach is expanding.
According to a report by the World Economic Forum, AI will create 97 million new jobs by 2025.
However, it’ll also displace 85 million jobs, creating both excitement and concern.
The Wall Street Journal covered a study on AI’s impact on white-collar jobs. It revealed that high-skilled workers aren’t immune to AI disruption.
Tasks involving data analysis and decision-making are increasingly automated.
But remember that AI’s not replacing jobs; it’s changing them. Many roles are being augmented by AI.
Workers are learning to collaborate with tools. This collaboration enhances productivity and creativity in so many sectors.
How Has AI Affected Jobs Over the Past Decade?
AI’s impact on jobs has been significant over the last ten years. We’ve seen a mix of job creation and displacement.
The effects haven’t been uniform across sectors. Some fields have embraced AI more rapidly than others.
We’ve witnessed changes in job roles and required skills. Let’s explore specific examples and compare initial fears with actual outcomes.
Examples of AI Implementation Across Various Sectors
Here are some examples of how AI is changing different industries:
Healthcare
Machine learning algorithms now assist in diagnosing diseases. They’re analyzing medical images with high accuracy.
AI helps predict patient outcomes and personalize treatment plans.
Doctors and nurses aren’t being replaced. They’re using AI to enhance their ability to provide quality care by letting it handle administrative tasks.
Finance
Algorithmic trading is now commonplace on Wall Street. Language models analyze market trends and make split-second decisions.
They’re also detecting fraudulent activities more efficiently than ever before.
Financial analysts are adapting their roles. They’re learning to work alongside AI systems.
They focus on strategy and complex decision-making, while AI handles data processing and pattern recognition.
Commerce
The retail sector has been transformed by AI-powered recommendation systems. E-commerce giants use AI to predict consumer behavior.
You can now create personalized shopping experiences and optimize inventory management.
Retail jobs have shifted towards customer experience and tech support.
AI takes care of inventory and logistics, while store associates focus on providing personalized service and solving complex customer issues.
Manufacturing
Workers are now performing repetitive tasks with high precision. Predictive maintenance systems reduce downtime and optimize supply chains and production schedules.
Many factory workers are becoming robot operators and maintenance technicians. They’re developing skills in programming and systems management.
The focus has shifted from manual labor to oversight and problem-solving.
Transportation
We’ve all seen self-driving vehicles like Teslas flying off the shelves.
But what’s more impressive is that it can analyze routes and manage traffic flow—improving safety and efficiency in logistics.
Drivers are learning to work with AI navigation and safety systems. The industry is preparing for a future where AI will play a larger role in vehicle operation.
Initial Fears vs. Real-World Outcomes
Early predictions about AI’s impact were often dire. Many feared widespread job losses. There were concerns about machines replacing human workers entirely.
But you know what? These fears haven’t fully materialized.
Instead, we’ve seen a more nuanced reality. Some jobs have indeed been automated. But many more have been augmented by AI.
New roles have emerged that we couldn’t have predicted a decade ago.
We’ve witnessed the rise of new professions. Data scientists, AI ethicists, and machine learning engineers are now in high demand.
These roles didn’t exist or were rare a decade ago.
The key outcome has been the changing nature of work. Routine tasks are increasingly automated.
Human workers focus on tasks requiring creativity, emotional intelligence, and complex problem-solving.
Fears of mass unemployment haven’t been realized. Instead, we’re seeing a need for reskilling and upskilling.
Workers are adapting to work alongside AI systems. They’re developing new competencies to remain relevant in the AI era.
AI’s Role in Enhancing Job Quality
While it’s inevitable that it can change the job landscape; it’s also improving work quality. Let’s explore how AI boosts efficiency and productivity.
We’ll also discuss ethical considerations and strategies to mitigate job displacement.
How AI Can Boost Job Efficiency and Enhance Worker Productivity
It is changing and improving workplace efficiency. The most basic is automating repetitive tasks, freeing workers for creative endeavors.
In customer service, AI chatbots handle routine inquiries. Human agents focus on complex issues, improving satisfaction rates.
AI greatly benefits data analysis. It processes vast amounts of information quickly, enabling businesses to make informed decisions faster.
Marketing teams use many tools to personalize campaigns and write content, resulting in higher engagement and conversion rates.
Healthcare professionals use AI for diagnosis support. It analyzes patient data, suggesting potential conditions.
Still, the doctors make final decisions, but it helps speed up the process. It’s reducing wait times and improving patient care.
A study by Accenture found AI could increase labor productivity by up to 40% by 2035
Workers aren’t replaced; they’re empowered. AI handles time-consuming tasks, allowing humans to focus on high-value work.
How to Ensure Ethical AI Use and Mitigate Job Displacement
The answer to this question requires a two-pronged approach: upskilling the workforce and implementing robust policy reforms.
Upskilling
Upskilling is essential in the AI era. It’s about equipping workers with new skills to remain relevant. Companies should invest in continuous learning programs.
These programs can focus on skills that complement AI, such as critical thinking and emotional intelligence.
Reskilling and upskilling are essential strategies—for all of those impacted, this is non-negotiable.
They help workers adapt to AI-driven changes. In fact, it was reported that 54% of employees will need significant reskilling because of these changes.
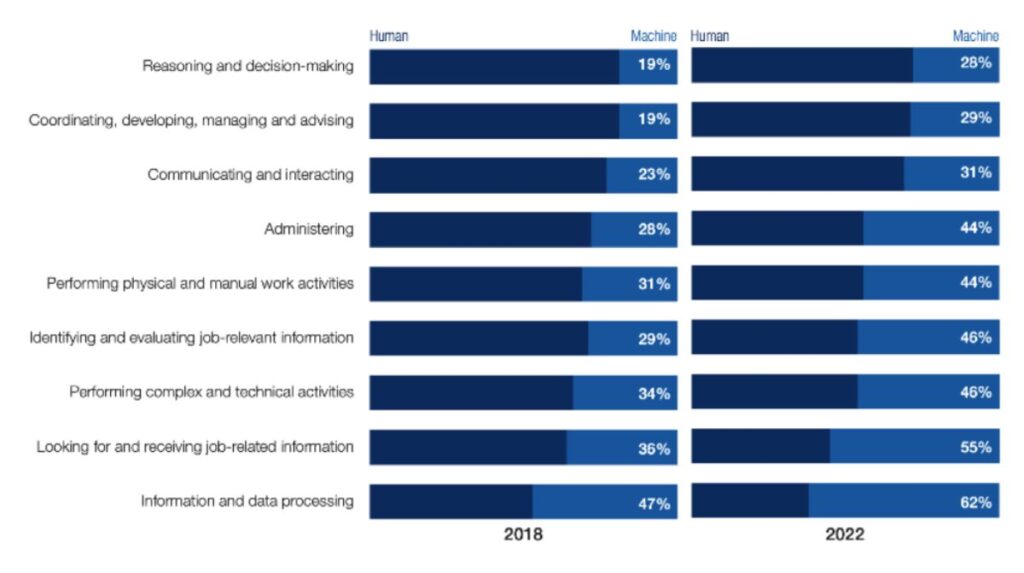
Workers must be proactive in their own development. They should seek opportunities to learn about AI and its applications in their field.
Online courses and workshops can be valuable resources for upskilling.
Governments can support upskilling efforts through education initiatives. They can offer subsidies for AI-related training programs.
This approach can help bridge the skills gap and reduce job displacement.
Policy reform
Policy reforms are equally important. They ensure AI is implemented ethically and with consideration for workers.
The European Union is taking a leading role in this area.
The EU Parliament is prioritizing safe, transparent, and non-discriminatory AI systems.
They’re emphasizing human oversight to prevent harmful outcomes. This approach balances innovation with worker protection.
Proposed regulations require AI systems to be traceable and fact-checked. Companies must document how their AI makes decisions.
This transparency helps identify and address potential biases.
The EU is also focused on environmental friendliness in AI development. They’re recognizing AI’s potential environmental impact.
This holistic approach ensures AI benefits society as a whole.
Other nations can learn from the EU’s example. They can develop similar frameworks tailored to their specific contexts.
These policies should address AI’s impact on employment and workers’ rights.
Collaboration between policymakers, businesses, and workers is key. They must work together to develop ethical AI guidelines.
These guidelines should balance innovation with job protection.
Conclusion
AI’s impact on jobs is complex and evolving. It’s creating challenges and opportunities.
Job displacement is a real concern, but new roles are emerging. The key lies in adaptation and preparation.
We must focus on developing skills that complement AI. Creativity, emotional intelligence, and complex problem-solving will remain uniquely human.
Education systems need to evolve to prepare future workers for an AI-integrated workplace.
Ethical considerations are paramount. We must ensure AI enhances rather than diminishes job quality.
Transparent and fair implementation is crucial for worker trust and engagement.
The future of work with AI is not predetermined. It depends on how we shape and guide its development.
By focusing on human-AI collaboration, continuous learning, and ethical implementation, we can create a future where AI enhances rather than threatens employment.
As we move forward, ongoing dialogue between policymakers, businesses, and workers is essential.
Together, we can navigate the challenges and harness the benefits of AI in the workplace. The goal is to create a future where technology and human potential thrive side by side.
