Quick quiz: How many seconds are in a week? In a leap year? In February?
Most people know how many seconds are in a day. Some even know the exact number: 86,400 seconds.
But did you know that not all days are the same length?
That’s right. Sometimes, a day can be 86,401 seconds long. Other times, it is 86,399 seconds.
This happens because of leap seconds. (we’ll explain what that means later.)
This blog explains everything about how many seconds are in a day, why there are 86,400 seconds in a day, how our clocks are tied to Earth’s movement.
We’ll also cover what leap seconds are and why they’re added, and how this all connects to the way we measure time today.
Let’s break it all down.
- A standard day has exactly 86,400 seconds. That’s calculated by multiplying 24 hours × 60 minutes × 60 seconds.
- Earth’s rotation gives us 24 hours, while the 60-based division of time comes from ancient civilizations.
- Leap seconds and daylight saving time can change how a day feels, but the Earth still spins through the same 86,400 seconds each day.
- Time can be quickly converted using a chain formula: hours → minutes → seconds. One hour has 3,600 seconds. Multiply by the number of hours, days, or weeks to get the total seconds.
- The definition of a second today is atomic, not astronomical. One second is based on the cesium-133 atom’s vibrations which is essential for GPS, satellites, and internet precision.
Quick Answer: 86,400 Seconds in a Day
Before diving deeper, let’s confirm the basics. How many seconds are there in a day?
The simple answer is 86,400 seconds in a day. But how do we get to that number? Let’s break it down step-by-step.
- Breakdown: 24 Hours × 60 Minutes × 60 Seconds
We start with what we already know:


Never Worry About AI Detecting Your Texts Again. Undetectable AI Can Help You:
- Make your AI assisted writing appear human-like.
- Bypass all major AI detection tools with just one click.
- Use AI safely and confidently in school and work.
- 1 hour has 60 minutes.
- 1 minute has 60 seconds.
So, if you want to find out how many seconds are in just 1 hour, you multiply:
→ 60 minutes × 60 seconds = 3,600 seconds.
Now, since a full day has 24 hours, you take that number and multiply again:
24 hours × 3,600 seconds = 86,400 seconds.
There’s also another way to calculate it. A day has 1,440 minutes (that’s 24 × 60), and each of those minutes has 60 seconds. So:
1,440 × 60 = 86,400 seconds.
This method also gives the same answer. This helps if you’re thinking in terms of minutes instead of hours.
Now let’s zoom out for a second — why is a day split into 24 hours?
It all comes down to Earth’s rotation. It takes about 24 hours for the planet to complete one full spin on its axis. That’s where the 24-hour day comes from.
But why divide hours into 60 minutes, and then again into 60 seconds?
That goes way back to the Babylonians, who used a base-60 (sexagesimal) number system.
They found 60 useful because it can be divided easily by many other numbers (like 2, 3, 4, 5, 6).
That’s why we still use 60-minute hours and 60-second minutes today.
To make this formula easier to remember:
1 hour = 3,600 seconds
1 day = 24 hours
So just think: 24 × 3,600 = 86,400 seconds
- The Formula Explained Simply
To find out how many seconds are in any time period, use this basic formula:
Time = Hours × Minutes × Seconds
Here’s how the logic works:
- Start with hours → multiply by 60 to get minutes
- Then multiply again by 60 to get seconds
It’s a chain of conversions from larger units to smaller ones.
Examples:
- Half a day (12 hours)
12 × 60 × 60 = 43,200 seconds - Quarter day (6 hours)
6 × 60 × 60 = 21,600 seconds - 1 hour
1 × 60 × 60 = 3,600 seconds
An easy way to remember it:
One hour has 3,600 seconds — just multiply by the number of hours you need.
Understanding Time Units

To fully grasp how many seconds are in a day (or in any span of time), it helps to understand the hierarchy of time units.
Time is structured from the largest blocks to the smallest:
Millennium → Century → Decade → Year → Month → Week → Day → Hour → Minute → Second
Each level connects to the next through consistent, though historically rooted, conversions:
- 1 minute = 60 seconds
- 1 hour = 60 minutes = 3,600 seconds
- 1 day = 24 hours = 1,440 minutes = 86,400 seconds
To understand how many seconds are in a day, we need to explore why the day is structured this way.
- The 24-hour day comes from the Earth’s rotation — one full spin takes roughly 24 hours.
- The 60-based system (for minutes and seconds) was inherited from ancient Babylonian mathematics, which used base-60 for its divisibility advantages.
- The 7-day week is a mix of religious tradition and lunar cycle approximations.
- Months and years are tied to the moon’s phases and Earth’s orbit around the sun, respectively.
Scientists moved from sundials (sun-shadow time tracker) and gears (mechanical time regulators) to atomic clocks.
Today, the second is defined not by the sun, but by physics.
Example:
1 second = the duration of 9,192,631,770 transitions of the cesium-133 atom.
This atomic definition keeps time very exact — which is important for GPS, the internet, and space travel.
Now, with this unit-based understanding, you can easily convert across formats, Ask AI:
For example:
- How many seconds in 2.5 days?
2.5 × 24 × 60 × 60 = 216,000 seconds - Convert 90,000 seconds to hours and minutes:
90,000 ÷ 3,600 = 25 hours
That’s 25 hours, or 1 day and 1 hour
- How many seconds in a leap year day?
Still 86,400 — but the extra day in February every 4 years means a leap year has: 366 × 86,400 = 31,622,400 seconds
Variations and Exceptions
So far, we’ve answered how many seconds are in a day with 86,400. But sometimes scientists add or subtract a leap second to keep atomic time in sync with Earth’s rotation.
Let’s break them down:
- Leap Seconds
Sometimes, scientists add or remove a second to keep our clocks in sync with Earth’s slightly irregular rotation. These are called leap seconds.
- A leap second can make a day 86,401 or 86,399 seconds long.
- The last leap second was added on December 31, 2016. It’s rare, but important for systems like GPS and satellites that need precise time.
- Daylight Saving Time (DST)
During DST changes, the clock jumps forward or backward:
- Spring: You “lose” an hour → 23-hour day
- Fall: You “gain” an hour → 25-hour day
But this only affects your local time, not the total number of seconds in Earth’s rotation.
- Solar Day vs Sidereal Day
- A solar day (what we follow) = 86,400 seconds
- A sidereal day (based on stars) = 86,164 seconds
The difference comes from Earth’s movement around the sun. A sidereal day is about 4 minutes shorter.
- Leap Years
A leap year adds one extra day in February, making 366 days instead of 365. Each day still has 86,400 seconds — it’s just that the year is longer, not the day.
- Time Zones
Time zones make it feel earlier or later depending on where you are, but they don’t change the actual number of seconds in a day.
So whether you’re in Tokyo or Toronto, the Earth still spins through 86,400 seconds per day.
Visual Conversion Chart

Time is made up of layers, from tiny milliseconds to full years. Here’s how those layers convert:
Starting with a day:
- 1 day → 24 hours → 1,440 minutes → 86,400 seconds
Now, seconds into larger time units:
- 86,400 seconds = 1 day
- 604,800 seconds = 1 week (7 days)
- ~2,628,000 seconds = 1 month (average 30.44 days)
- 31,536,000 seconds = 1 year (365 days)
From smaller units to a second:
- 1,000 milliseconds = 1 second
- 1,000,000 microseconds = 1 second
Example:
A 15-minute coffee break = 900 seconds.
A 2-hour movie = 7,200 seconds.
Comparison Table: Seconds in a Day, Week, Month
| Unit | Formula | Total Seconds |
| 1 Day | 24 × 60 × 60 | 86,400 |
| 1 Week | 7 × 24 × 60 × 60 | 604,800 |
| Month (30 days) | 30 × 24 × 60 × 60 | 2,592,000 |
| Month (31 days) | 31 × 24 × 60 × 60 | 2,678,400 |
| February (28 days) | 28 × 24 × 60 × 60 | 2,419,200 |
| February (29 days) | 29 × 24 × 60 × 60 | 2,505,600 |
| 1 Year (365 days) | 365 × 24 × 60 × 60 | 31,536,000 |
| Leap Year (366 days) | 366 × 24 × 60 × 60 | 31,622,400 |
If you want faster answers without multiplying days × hours × minutes × seconds, ask AI Chat.
Example:
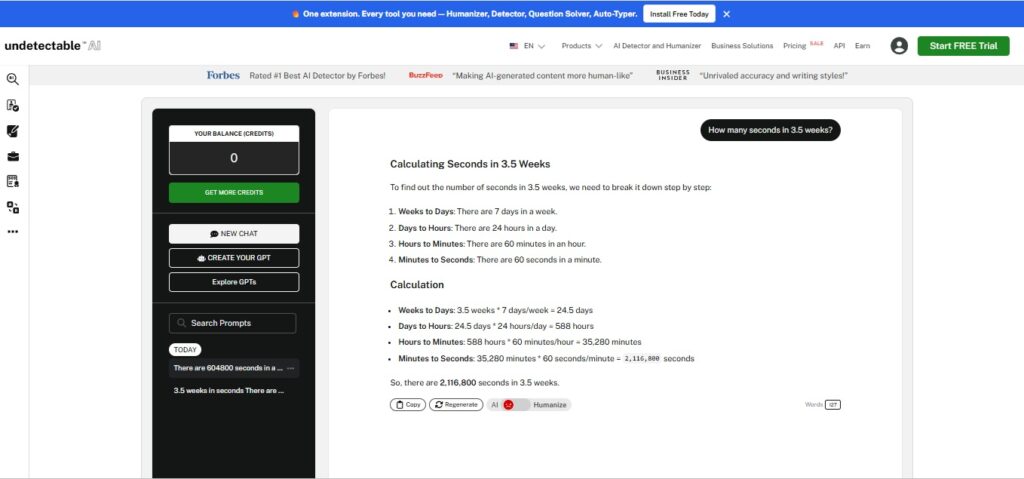
This tool can instantly calculate custom time spans, adjust for leap years, or convert milliseconds to hours without error.
Check out our AI Detector and Humanizer right in the widget below!
FAQs About Time and Seconds
Are There Always 86,400 Seconds in a Day?
No. Most days have 86,400 seconds, but sometimes a leap second is added or subtracted due to slight changes in Earth’s rotation.
How Many Seconds in a Week or Month?
It depends on the number of days. A week has 604,800 seconds.
A 30-day month has 2,592,000 seconds, while a 31-day month has 2,678,400. February has 2,419,200 seconds in a regular year and 2,505,600 in a leap year.
What’s the Difference Between Solar Day and Civil Day?
A civil day is always 24 hours by clock.
A solar day is slightly longer, about 24 hours and 4 seconds, based on Earth’s true rotation. That difference is why leap seconds and calendar adjustments exist.
Final Thoughts
So, how many seconds are in a day?
Most of the time, 86,400. But as you’ve seen, time isn’t as rigid as we assume.
- Ever thought about why we trust machines to split time into such perfect slices—while the planet itself moves a little differently each day?
- Why do we still use ancient Babylonian math to structure our minutes and seconds?
- What does it say about us that we rely on atomic vibrations to define something as human as time?
Understanding time down to the second is about seeing history, science, and nature.
The clock we see every day has a number is a chain of logic, tradition, and physics.
And the real question might not be how many seconds are in a day—but what are you doing with them?
Make every second count—use Undetectable AI to write smarter and faster.
