Learning about pronouns and how they function in English to write clear and correct sentences and communicate clearly, whether orally or in writing, is very important.
Among the eight pronouns, one type of pronoun is an object pronoun.
Although an object pronoun receives the action, most English learners misunderstand or ignore them entirely.
After reading this article, you will be able to answer the question: what is an object pronoun and how they are different from subject pronouns.
You will also learn more about the position of object pronouns in a sentence structure and how you would apply them in many contexts.
Key Takeaways
- Object pronouns indicate the receiver of the action of a verb as well as pronouns that follow a preposition in a sentence.
- Object pronouns are different from subject pronouns that take action (i.e, he vs. him).
- Object pronouns usually go after verbs and prepositions, not before.
- An object pronoun is direct when it answers “what?” or “whom?”; indirect when it answers “to whom?” or “for whom?”.
- In another language such as Spanish, object pronouns have different rules and often appear before the verb.
- Resources such as grammar checkers and AI writing assistants are valuable resources to help students identify pronoun errors and correct them.
What Are Object Pronouns?

An Object pronoun is a type of personal pronoun that replaces nouns that receive an action in a sentence.
An object pronoun is a grammatical object, or in the case of a subject-object verb, a noun that is not acting but is being acted upon and has the same function as an object pronoun.
By way of example, where we would normally write a noun, such as “Sarah” in every sentence, ∙ “I saw Sarah. I called Sarah.


Never Worry About AI Detecting Your Texts Again. Undetectable AI Can Help You:
- Make your AI assisted writing appear human-like.
- Bypass all major AI detection tools with just one click.
- Use AI safely and confidently in school and work.
I thanked Sarah,” we can use an object pronoun “her” to delete noun repetition: “I saw her. I called her. I thanked her.”
Being an object pronoun is part of a pronoun case system meaning that an object pronoun has a noun role.
The pronoun form will change depending on its grammatical usage in a sentence.
Object pronouns are primarily located after two types of functions: action verbs or prepositions, and they always refer to a noun used before the referred word, or to contextually understand a noun (in this case, a pronoun; the reference noun is not a person, but an object).
List of Common Object Pronouns
Object pronouns substitute nouns that act as objects in a sentence, as either the theme recipient of a verb action or following a preposition.
The reason for sending a message more cohesively through pronouns (and reducing repetition) will vary in form depending on whether it is a first person, second person, or third person plural.
Here is a list of the most functionally common object pronouns in English by person and number:
| Person | Singular | Plural |
| First Person | Me | Us |
| Second Person | You | You |
| Third Person | Him, Her, It | Them |
Each of these object pronouns has the equivalent subject pronoun, which performs the action of the verb clause.
Pronoun Case: Subject vs. Object
Pronouns help you organize or construct your sentence in order to distinguish between the subject and the object.
In English terms, pronoun case refers to the pronoun form depending on its usage in a sentence, in terms of whether the pronoun implies it takes a subject or takes object position.
- A subject pronoun interface helps or uses the action of a verb. Some examples include: I, you, he, she, it, we, and they. These are some examples of the pronouns you’ll most likely find at the beginning of a sentence:
- She runs a mile every morning.
- They are going to the conference.
- An object pronoun, on the other hand, receives the action. These include: me, you, him, her, it, us, and them. These pronouns often appear after verbs or prepositions in sentences:
- He called me yesterday.
- We sent the package to them.
It is important not to confuse these two cases, as mixing them up will always lead to grammatical errors.
The example above, “Her went to the store” is the misuse of an object pronoun (her) in a subject position, so it is utterly wrong.
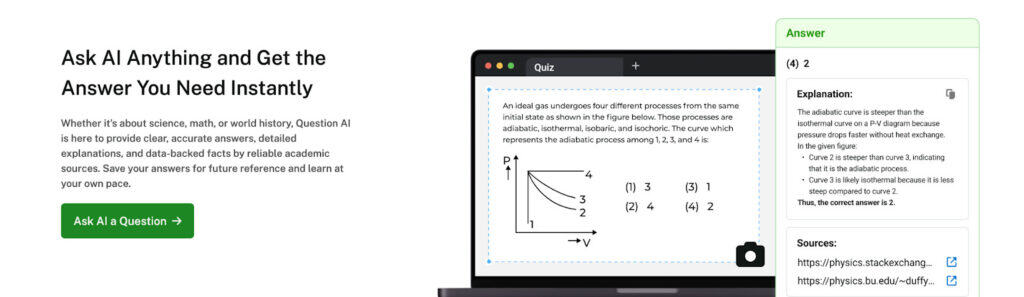
It takes practice to reinforce this for learners of all bands. You can use our Undetectable AI’s Ask AI to learn more and understand object pronouns.
This tool allows students to quiz themselves on subject and object uses, sentence structure, and receive real-time individualized feedback!
How to Use Object Pronouns in Sentences
Using an object pronoun correctly in a sentence also depends on understanding the function of the object pronoun in relation to the act of the verb and any other variables present in the sentence.
Since object pronouns receive the action, and not perform it, the placement or role for context is always governed in relation to how grammar works to clarify thought and express flow.
- Direct and Indirect Objects
In order to figure out if an object pronoun is direct or indirect, you will have to pay more attention to its functionality in the sentence.
- What is a direct object pronoun? A direct object pronoun responds to the question “what?” or “whom?” to the verb.
Example: She invited him to the event. (“Him” performs the action of being invited.)
- What is an indirect object Pronoun? An indirect object pronoun gives “to whom” or “for whom” the action occurred.
Example: We gave her a gift. (“Her” benefits from the action, but is not the giving object.)
It is important to determine whether the pronoun is a direct or indirect object for the organization of the sentence and for identifying the common mistakes.
- Common Sentence Structures
Most object pronouns follow a pattern: Subject + Verb + Object Pronoun. Here are some examples of common variations:
- I saw them at the station.
- He helped me with the assignment.
- They invited us to the launch.
These patterns hold across all tenses and in all forms, whether simple sentences, more complex sentences, or their variations and combinations.
- Position After Verbs and Prepositions
- Object pronouns can always be placed right after a verb. They can also be placed after a preposition. They should never be placed before the verb or preposition.
Example:
- You can trust me (follows verb)
- This message is for you (follows preposition)
- Object pronouns are still directed according to the verb regardless of whether they’re in a compound verb form or infinitive structure.
Example:
- She wants him to stay longer.
- They asked us to respond quickly.
Improper placement can either cause confusion in a sentence or result in a sentence that sounds “wonky.”
If you are struggling to place words correctly when writing, you may not see it as much of an issue but if you are a professional writer or a student, you would take note of every possible mistake in order to pass the right information across.
In situations where you are unsure how to use object pronouns correctly especially with longer sentences, we encourage you to use our Undetectable AI’s AI Grammar Checker.
Our Grammar checker can assess your text for violations where a pronoun is a misuse, where you have broken the subject-object agreement, or whether your subject-object pronouns are awkward, or just plain wrong!
Object Pronouns vs Subject Pronouns
Differentiating between object and subject pronouns is one of the most difficult tasks for people learning English.
While they may look similar, interchangeable at times for learners, each acts in its grammatical manner in the sentence.
How to Tell Them Apart
We can differentiate between a subject and an object pronoun majorly by the function they play in a sentence.
- Subject pronouns perform the action.
Examples: I, you, he, she, it, we, they - Object pronouns receive the action.
Examples: me, you, him, her, it, us, them
When a pronoun is found before the verb and is acting as the agent of the verb, it is likely a subject pronoun. If it is after the verb or follows a preposition, it will function as an object.
Swapping Pronouns to Test for Accuracy
One good method to see if you are using the correct pronoun is to replace it with a full noun and see if the sentence still makes sense and then replace the noun back with the correct pronoun form.
We shall test this with some examples.
- Incorrect: Her called me yesterday.
Replace with a noun: Sarah called me yesterday.
Clearly, “Sarah” is the subject, so the correct pronoun should be she; She called me yesterday.
- Incorrect: Can you help I with this?
Replace with a noun: Can you help John with this?
Since “John” is the object here, the correct pronoun is me; Can you help me with this?
Examples of Both in Use
Here are examples that show subject and object pronouns functioning within the same sentence:
- She (subject) handed me (object) the folder.
- They (subject) invited us (object) to the seminar.
- I (subject) told him (object) the news.
- We (subject) helped her (object) carry the boxes.
Examples of Object Pronouns in Action

Understanding the definition and rules with respect to object pronouns is just one part of knowing how to use them.
To understand how a pronoun works in real language, it is important that we examine sentences using object pronouns in different types of sentence constructions.
- Simple Sentences
In the simplest sentences, we can see that object pronouns will always be placed after a verb and whether they are being seen, met, thanked, or given something, etc., they are serving as a receiver.
Some examples:
- She saw him at the library.
- I met them after the conference.
- We appreciate your help.
- They offered me a seat.
Sentences like these are used in everyday discourse and basic writing, and they are simple to make and will work mathematically when we think to replace the proper noun e.g. (John, Maria, and the Group) object pronouns give us the advantage to create a short hand construction, eliminating words where meaning is not altered whatsoever.
- Compound and Complex Constructions
Object pronouns will always serve their purpose despite the positions getting less clear, like in complex/compound sentences, because of adding clauses in the information, multiple subjects in the information, or multiple tenses in the information.
Examples:
- She thanked us after they had concluded the meeting and handed me a copy of their notes.
- I know him; we just don’t see each other as often as we used to.
You can see how well the object pronouns remain coherent, relatively naturalized cause of the lengthy sentences.
From the examples given above, you can now see how natural the use of those object pronouns is because of the length of the sentence.
Additionally, while the sentences are more complex, the object pronoun persists after an action verb, serving as a grammatical object while maintaining a consistent covert presence over longer constructions.
- Object Pronouns in Questions
Object pronouns are regularly placed in direct and indirect questions, especially in cases of giving and receiving information, an action, or an emotion.
When asking questions, you need to make sure the pronouns are marked correctly after the verb or preposition per the appropriate clause.
Some examples are:
- Will you help me with this task?
- Did they inform you about the schedule change?
- Should I alert him about what happened?
- Whose turn is it to drop us off at the national airport?
Ready to see the difference? Launch our AI Detector and Humanizer in the widget below!
Final Thoughts
When asked what is a object pronoun, after reading this article, you can never be wrong again.
Let’s run through it before we go; Object pronouns are a small part of speech, but many aspects of sentence fluency, clarity, and even grammar can depend on having object pronouns as intended.
Object pronouns will always take the role of receiving the action in a sentence.
At the same time, the difference between subject and object pronouns is sometimes slight, but can still be negatively impactful in an academic or professional situation.
The wrong use of a subject pronoun or object pronoun will lead to confusion or loss of meaning.
Whether you are a student or teacher wanting to assess understanding of pronouns, our Undetectable AI-enabled Ask AI tool can help you create practice questions specific to your needs and can evaluate your knowledge and understanding of pronouns in real time.
Our Grammar Checker can also be used to generate real-time feedback on spelling, grammar, and usage errors as you write.
After the full read, even if asked what is a direct object pronoun in spanish, I believe you would have no problems answering.
Need help polishing your writing? Try Undetectable AI to make your grammar clear, natural, and truly yours.
