A paragraph is a lot like a family dinner.
Everyone’s supposed to be talking about the same thing, but if Uncle Joe starts describing his fishing trip while Aunt Janice argues about politics, the dinner turns into a chaotic nightmare.
Writing works the same way. When your sentences don’t stick to one main idea, your reader gets lost, or worse, bored.
The problem is, nobody really teaches us how to build a paragraph. However, paragraphs aren’t complicated once you see what they’re made of.
So, what is a paragraph exactly?
Let’s break it down.
Key Takeaways:
- A paragraph is a group of two or more sentences that expand on the same idea.
- There are four parts of a paragraph: topic, supporting sentences, examples, and conclusion.
- We also have four types of paragraphs, i.e., narrative, descriptive, persuasive, and expository.
- To write a strong paragraph, you need to make sure it is clear and keeps your reader interested.
What Is a Paragraph?

A paragraph is merely a bunch of sentences that complement each other to explain an idea.
Yup, that’s it. It’s not five sentences and definitely not a magic number. Just a small unit of writing that has a purpose.
Paragraphs act as a pause in the rhythm of your writing. It gives your reader a chance to breathe, to process one idea before moving on to the next.


Never Worry About AI Detecting Your Texts Again. Undetectable AI Can Help You:
- Make your AI assisted writing appear human-like.
- Bypass all major AI detection tools with just one click.
- Use AI safely and confidently in school and work.
Without paragraphs, everything would blur into one endless stream of text.
A good paragraph isn’t defined by how many sentences it has.
Sometimes it’s three, sometimes it’s eight.
What matters is that all the sentences belong together and point in the same direction.
If they start wandering off, that’s a sign you’re not looking at one paragraph anymore, and it’s time to stop.
Parts of a Paragraph
(Almost) Everyone knows what a paragraph is. But what most of us don’t know is that it contains four main parts.
These parts are what hold a paragraph together.
1. Topic Sentence
What is a topic sentence in a paragraph? It is where the paragraph begins.
The topic sentence introduces the main idea, i.e., the one point you’re about to develop. It doesn’t need to be extra, but it should be clear enough that your reader knows what to expect.
For example, if you’re writing a body paragraph in an essay, the topic sentence works like a signpost.
It shows where you are heading before you discuss the details.
2. Supporting Sentences
Once you’ve put your main idea on the table, you can’t just leave it sitting there.
Your reader needs to know what you mean, and that’s where supporting sentences come in.
Supporting sentences give shape and weight to your paragraph.
They might explain a concept in simpler terms, add a bit of context, or connect your point to something your reader already understands.
3. Evidence & Examples
Have you ever heard of the “show, don’t tell principle?” It applies to all forms of writing. In fact, it’s what separates good writing from bad writing.
Evidence and examples give your paragraph weight.
Depending on what you’re writing, this could mean facts, data, quotes, or even a quick story or scenario.
4. Concluding Sentence
You cannot end your paragraph abruptly. It needs a conclusion. Every paragraph needs one.
A concluding sentence ties everything back to the main idea and prepares the reader for what comes next.
It doesn’t always have to summarize, but it should leave the paragraph feeling finished.
Do it well, and your writing will always flow smoothly.
I bet you are surprised that a seemingly simple paragraph has this many technicalities. But now that you know this, it’s pretty easy to notice.
Usually, when I have trouble writing a decent paragraph, I turn to Undetectable AI’s AI Paragraph Generator.
Type in your topic, choose your desired tone, length, and the number of paragraphs you need.
You will get the results within seconds.
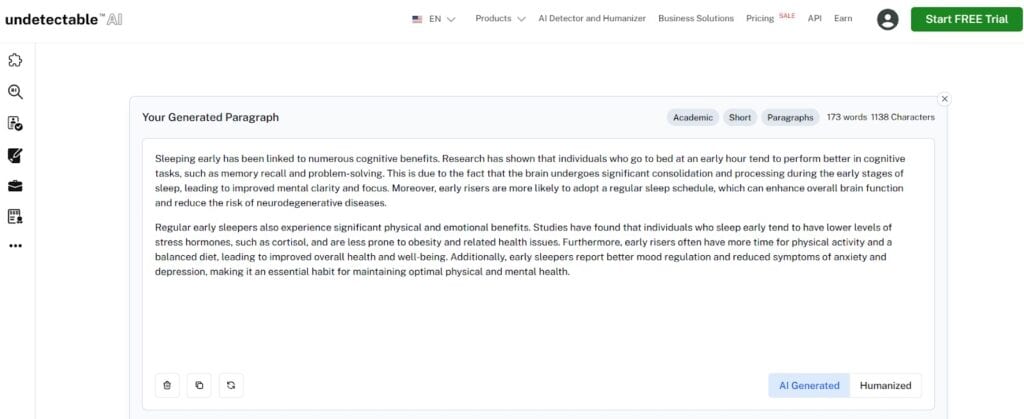
Isn’t that impressive?
Once you use it a couple of times, it will help you learn how paragraphs are structured. Soon, questions like “What is a introduction paragraph?” will be the least of your confusions.
To guarantee your writing doesn’t just fizzle out but ends with a resonant point, you can use our Conclusion Generator to summarize your key findings into a clear and well-structured final part for any article.
This tool helps you tie back to your original topic sentence while providing the human-like closure that keeps your audience engaged until the very last word.
Types of Paragraphs
Different paragraphs have different purposes.
We use some to tell a story and others to describe. Some explain, while others persuade.
Let me introduce you to the four most common types of paragraphs.
1. Narrative Paragraphs
A narrative paragraph tells a story. It is based on action and sequence and shows what happened first, what came next, and how it ended.
Developing a cohesive narrative that flows logically from a simple core idea can be challenging for writers, which is where Undetectable AI’s Story Generator excels.
Our tool can rapidly illustrate how a single prompt can expand into a full, well-developed narrative paragraph with clear action and sequence, using our Undetectable AI’s Story Generator.
These paragraphs are a common part of personal writing, stories, or case studies where the reader needs to follow along step by step.
2. Descriptive Paragraphs
A descriptive paragraph in an essay or any other form of writing focuses on detail.
Instead of telling a sequence of events, it lingers on the look, sound, or feel of something so the reader can picture it clearly.
These paragraphs are useful in creative writing but also in everyday contexts like product descriptions or travel blogs.
3. Expository Paragraphs
An expository paragraph explains an idea or gives information. It lays things out in a logical way to answer questions like how or why.
Think of it as an explanation of what a body paragraph is.
A body paragraph is also a type of expository paragraph that develops one main point with explanation, facts, or examples.
4. Persuasive Paragraphs
A persuasive paragraph is built to convince. It makes a claim and then works to get the reader on board. It can use evidence, logic, or an emotional appeal.
These paragraphs appear in opinion writing, advertising, and argumentative essays.
Understanding the different types of paragraphs is the easier part.
The real trick is converting one type of paragraph into another.
Excuse me, for I just exaggerated the bit. It’s not all that difficult once you have done it a few times.
But for those who are new to it, I highly recommend using the Paragraph Rewriter by Undetectable AI to make AI write like you.
This tool can rewrite a paragraph in any chosen tone. You can pick from academic, creative, professional, casual, and formal.
How to Write Strong Paragraphs

A strong paragraph is clear and keeps your reader interested. There’s no rocket science involved.
You just have to take care of a few things.
- The “one-thing rule”
Every paragraph should be about one thing. Not two, not three. Before you write, jot down the point in a short phrase (e.g., “coffee helps me focus”).
That phrase is your anchor. If a sentence doesn’t connect back to it, cut or move it.
- Avoid fillers
Don’t waste the first line with warm-ups like “It is important to note…” or “In today’s world…” (It’s AI sentence structure and can be detected as ChatGPT content). Jump straight in.
The first sentence sets the tone, and if it’s sharp, your reader will trust you enough to keep going.
- Don’t worry about the length
I’ve seen people waste too much time wondering how many sentences a paragraph should have. Surprise, surprise. You’re stressing over the wrong thing!
Focus on making your paragraph feel complete instead. You need one sentence to introduce, another few to build, and one to land.
Sometimes that’s three sentences, sometimes it’s ten.
- Show, don’t just tell
i. Phones distract people.
ii. An average person checks their phone 144 times a day.
The first sentence falls flat because it explains without something concrete.
The second hits harder because it doesn’t pile on abstract words. It used a number. Readers remember specifics.
- Land the plane
A paragraph that just fizzles out feels unfinished. You don’t always need a formal “concluding sentence,” but you do need closure.
Make your last line about what you want the reader to take away from the paragraph.
If you’re struggling to rewrite or restructure your paragraph without losing its meaning, the AI Rewording Tool can help.
It lets you rephrase entire paragraphs with better clarity, tone, and structure. Perfect for turning a messy draft into something clean, coherent, and natural.
- Check for grammar mistakes.
Good grammar makes your writing clear. Sometimes we get so lost in the flow that we forget about sounding grammatically correct. But that’s okay. That’s fixable.
Always run your writing through the Grammar Checker to fix any grammar mistakes you may have missed.
Also, to make your writing feel more natural and less robotic, try Undetectable AI’s AI Humanizer for that final human touch.
Examples of Paragraphs
Paragraphs this, paragraphs that. I’ve been going on and on about what is an introduction paragraph, what is a conclusion paragraph (blah, blah).
What you’re yet to see are examples to understand what I actually mean.
Narrative Paragraph Example
“I still remember the first time I went skating. At first, even standing up without losing my balance was a challenge. Every time I tried, it felt like I had no control over the wheels beneath my shoes.
However, after the first few shaky seconds, my trainer helped me stand steadily. And in no time, I felt the rush of moving forward on my own.”
Descriptive Paragraph Example
“The room smelled of old paper and dust. I could see the sunlight filtering through the tall windows and landing in golden circles on the mahogany study table where my friend was reading a book.“
Expository Paragraph Example
“Drinking enough water during the day helps improve focus and energy.
When your body is even slightly dehydrated, it can make you feel tired and less alert.
Studies show that staying hydrated supports better memory, concentration, and even mood.”
Persuasive Paragraph Example
“Students should avoid using their phones while studying. Research has proven that it can take several minutes to refocus after checking a message.
Turning the phone off or leaving it in another room makes study time more productive and less stressful.”
As you can see, each type of paragraph is written in a different way. Many people (including me) struggle when we have to deliver the same message in a different tone.
You know, say the same thing but make it professional. I mean, how do I tell my boss I’m quitting the job because I hate him in a professional tone?
Fortunately, I don’t have to do it on my own. Instead, I use Undetectable AI’s Writing Style Replicator.
And if you ever want to write content that slips past AI detectors while staying readable, give the AI Stealth Writer a shot.
Check out our AI Detector and Humanizer right in the widget below!
FAQSs
What is a paragraph?
A paragraph is a group of sentences that focus on one main idea. It gives the reader a chance to digest one idea before moving on to the next.
How many sentences make a paragraph?
There’s no fixed rule, but most paragraphs have 3-6 sentences.
The goal is to explain your idea without overwhelming the reader, regardless of how many sentences it takes.
Can a paragraph be just one sentence?
Absolutely. If you can use just one sentence to deliver a point with emphasis, you can end your paragraph there.
One-sentence paragraphs are more common in online writing or advertising, like blogs, social media, etc.
What’s the ideal length for online paragraphs?
Shorter paragraphs work best for online content.
You can ideally have 2-4 sentences per paragraph, so the text feels easy to scan and doesn’t overwhelm the reader’s eyes.
Conclusion
Now that you know what is a paragraph, you see they are not complicated. You just have to keep one idea from crashing into another.
Of course, we can’t always guarantee that. But for those rainy days, you have Undetectable AI’s tools.
It can help you sort out your messy paragraphs while following a consistent tone.
Use Undetectable AI’s Paragraph Generator and Paragraph Rewriter to structure clear, organized thoughts.
Then rely on the Grammar Checker and AI Writing Style Replicator to keep everything polished and consistent.
Just give it a try and you’ll thank me later!
With Undetectable AI, your writing won’t just make sense, it will stand out.
